Introduction
When it comes to choosing a firewall solution for your network, two prominent open-source options often come to mind: pfSense CE and OPNsense. Both are highly capable, feature-rich platforms that offer extensive functionality and flexibility. This guide aims to help you make an informed decision by comparing these two firewalls across various dimensions.
Brief History
pfSense CE was originally forked from the m0n0wall project in 2004 by Chris Buechler and Scott Ullrich. It has since grown into a popular and robust firewall solution maintained by Netgate, a US-based company. Recently, Netgate has introduced pfSense Plus, which has led to concerns that the CE version may not receive as much attention and development focus.
OPNsense was forked from pfSense CE in 2015 by Deciso, a Dutch company. The fork was driven by a desire to create a more transparent and community-driven project. Notably, when the m0n0wall project ended in 2015, its founder Manuel Kasper recommended OPNsense as the successor to continue the m0n0wall philosophy.
Ownership and Development
pfSense CE
- Owned by Netgate, a US-based company.
- Follows a more centralised development model with significant contributions from Netgate.
- Recent introduction of pfSense Plus has shifted some focus away from the CE version.
- Strong community involvement with forums, mailing lists, and a comprehensive documentation wiki.
OPNsense
- Owned by Deciso, a Dutch company.
- Emphasises a community-driven approach with transparency in development and decision-making.
- Active community with regular updates and extensive documentation.
Core Features Comparison
Firewall and Routing
- pfSense CE: Offers stateful packet filtering, NAT, and advanced routing capabilities. Supports IPv6 and provides robust traffic shaping.
- OPNsense: Similarly provides stateful packet filtering, NAT, and advanced routing. It also includes IPv6 support and comprehensive traffic shaping.
Security Features
- pfSense CE: Includes support for Snort and Suricata IDS/IPS, multiple VPN options (IPsec, OpenVPN, WireGuard), and robust security protocols.
- OPNsense: Offers IDS/IPS via Suricata, multiple VPN options (IPsec, OpenVPN, WireGuard), and strong security protocols. It also includes built-in two-factor authentication.
User Interface and Usability
User Experience
- pfSense CE: Known for its straightforward and functional web interface. While powerful, it can be complex for new users.
- OPNsense: Features a modern, user-friendly web interface that is often praised for its intuitive design and ease of use.
Documentation and Support
- pfSense CE: Comprehensive documentation available, along with active community forums and commercial support options from Netgate.
- OPNsense: Extensive documentation and a helpful community forum. Deciso also offers commercial support and professional services.
Performance and Scalability
Hardware Requirements
- pfSense CE: Runs on a wide range of hardware, from small appliances to enterprise-grade servers. Minimum specs are modest, but performance scales with better hardware.
- OPNsense: Similarly flexible with hardware, supporting a range from small devices to powerful servers. Performance is dependent on the hardware capabilities.
Performance Metrics
- pfSense CE: Known for its high performance and reliability in various network environments.
- OPNsense: Also delivers strong performance, with many users reporting excellent throughput and stability.
Extensibility and Customisation
Plugins and Packages
- pfSense CE: Offers a variety of plugins and packages for additional functionality, such as pfBlockerNG and Squid.
- OPNsense: Provides a rich plugin system, including features like the Acme client for Let’s Encrypt, HAProxy, and more.
API and Automation
- pfSense CE: Does not have an official REST API, limiting options for automation and integration with other systems.
- OPNsense: Features a robust API, allowing for extensive automation and integration capabilities.
pfSense CE Plugins
Note: since this is a comparison between pfsense Community Edition and OPNsense, pfSense+ packages have been omitted from the list.
| Package Name | Description |
|---|---|
| acme | Automated Certificate Management Environment, for automated use of LetsEncrypt certificates. |
| apcupsd | “apcupsd” can be used for controlling all APC UPS models It can monitor and log the current power and battery status, perform automatic shutdown, and can run in network mode in order to power down other hosts on a LAN |
| arping | Broadcasts a who-has ARP packet on the network and prints answers. |
| arpwatch | This package contains tools that monitors ethernet activity and maintains a database of ethernet/ip address pairings. It also reports certain changes via email. |
| Avahi | Avahi is a system which facilitates host and service discovery in local networks via mDNS (Multicast DNS) and DNS-SD (DNS Service Discovery). This package allows mDNS/DNS-SD protocols to work across multiple LAN segments. mDNS/DNS-SD is known in Apple circles as “Bonjour” and is part of the Zeroconf suite of protocols. |
| Backup | Tool to Backup and Restore files and directories. |
| bandwidthd | BandwidthD tracks usage of TCP/IP network subnets and builds html files with graphs to display utilization. Charts are built by individual IPs, and by default display utilization over 2 day, 8 day, 40 day, and 400 day periods. Furthermore, each IP address’s utilization can be logged out in CDF format, or to a backend database server. HTTP, TCP, UDP, ICMP, VPN, and P2P traffic are color coded. |
| bind | pfSense GUI for BIND DNS server |
| cellular | pfSense GUI for Cellular Cards Currently it supports certain Huawei models. |
| Cron | The cron utility is used to manage commands on a schedule. |
| darkstat | darkstat is a network statistics gatherer. It’s a packet sniffer that runs as a background process on a cable/DSL router, gathers all sorts of statistics about network usage, and serves them over HTTP. |
| Filer | Allows you to create and overwrite files from the GUI. |
| freeradius3 | A free implementation of the RADIUS protocol. Supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, LDAP, Kerberos. |
| frr | FRR routing daemon for BGP, OSPF, and OSPF6 Conflicts with Quagga OSPF and OpenBGPD. These packages cannot be installed at the same time. |
| FTP_Client_Proxy | Basic FTP Client Proxy using ftp-proxy from FreeBSD. |
| haproxy | The Reliable, High Performance TCP/HTTP(S) Load Balancer. This package implements the TCP, HTTP and HTTPS balancing features from haproxy. Supports ACLs for smart backend switching. |
| haproxy-devel | The Reliable, High Performance TCP/HTTP(S) Load Balancer. This package implements the TCP, HTTP and HTTPS balancing features from haproxy. Supports ACLs for smart backend switching. |
| iperf | Iperf is a tool for testing network throughput, loss, and jitter. |
| LADVD | Send and decode link layer advertisements. Support for LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol), CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol), EDP (Extreme Discovery Protocol) and NDP (Nortel Discovery Protocol). |
| LCDproc | LCD display driver. |
| Lightsquid | LightSquid is a high performance web proxy reporting tool. Includes proxy realtime statistics (SQStat). Requires Squid package. |
| lldpd | lldpd provies support for the 802.1ab Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP), as well as support for several proprietary discovery protocols including Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), Extreme Discovery Protocol (EDP), Foundry Discovery Protocol (FDP), and Nortel Discovery Protocol (NDP / SONMP). |
| mailreport | Allows you to setup periodic e-mail reports containing command output, and log file contents |
| mtr-nox11 | Enhanced traceroute replacement. mtr combines the functionality of the traceroute and ping programs in a single network diagnostic tool. |
| net-snmp | A GUI for the NET-SNMP Daemon. |
| Netgate_Firmware_Upgrade | Provide a mechanism to update firmware of Netgate hardware |
| nmap | Nmap is a utility for network exploration or security auditing. It supports ping scanning (determine which hosts are up), many port scanning techniques (determine what services the hosts are offering), version detection (determine what application/service is running on a port), and TCP/IP fingerprinting (remote host OS or device identification). It also offers flexible target and port specification, decoy/stealth scanning, SunRPC scanning, and more. |
| node_exporter | Prometheus exporter for machine metrics |
| Notes | Track things you want to note for this system. |
| nrpe | pfSense software package GUI for Nagios NRPE nrpe is used to execute Nagios plugins on remote hosts and report the results to the main Nagios server. From the Nagios homepage: Allows you to execute “local” plugins (like check_disk, check_procs, etc.) on remote hosts. The check_nrpe plugin is called from Nagios and actually makes the plugin requests to the remote host. Requires that nrpe be running on the remote host (either as a standalone daemon or as a service under inetd). |
| ntopng | ntopng (replaces ntop) is a network probe that shows network usage in a way similar to what top does for processes. In interactive mode, it displays the network status on the user’s terminal. In Web mode it acts as a Web server, creating an HTML dump of the network status. It sports a NetFlow/sFlow emitter/collector, an HTTP-based client interface for creating ntop-centric monitoring applications, and RRD for persistently storing traffic statistics. |
| nut | Network UPS Tools provides support for monitoring of Uninterruptible Power Supplies. It supports UPS units attached locally via USB or serial, and remote units via the SNMP protocol, the APCUPSD protocol or the NUT protocol. |
| Open-VM-Tools | VMware Tools is a suite of utilities that enhances the performance of the virtual machine’s guest operating system and improves management of the virtual machine. |
| openvpn-client-export | Exports pre-configured OpenVPN Client configurations directly from pfSense software. |
| pfBlockerNG | Manage IPv4/v6 List Sources into ‘Deny, Permit or Match’ formats. GeoIP database by MaxMind Inc. (GeoLite2 Free version). De-Duplication, Suppression, and Reputation enhancements. Provision to download from diverse List formats. Advanced Integration for Proofpoint ET IQRisk IP Reputation Threat Sources. Domain Name (DNSBL) blocking via Unbound DNS Resolver. |
| pfBlockerNG-devel | pfBlockerNG-devel is the Next Generation of pfBlockerNG. Manage IPv4/v6 List Sources into ‘Deny, Permit or Match’ formats. GeoIP database by MaxMind Inc. (GeoLite2 Free version). De-Duplication, Suppression, and Reputation enhancements. Provision to download from diverse List formats. Advanced Integration for Proofpoint ET IQRisk IP Reputation Threat Sources. Domain Name (DNSBL) blocking via Unbound DNS Resolver. |
| pimd | PIMD Multicast Routing. Lightweight, stand-alone implementation of Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode. Conflicts with Quagga OSPF. These packages cannot be installed at the same time. |
| RRD_Summary | RRD Summary Page, which will give estimated month-over-month traffic passed In/Out during the specified period. |
| Service_Watchdog | Monitors for stopped services and restarts them. |
| Shellcmd | The shellcmd utility is used to manage commands on system startup. |
| siproxd | Proxy for handling NAT of multiple SIP devices to a single public IP. |
| snmptt | SNMPTT (SNMP Trap Translator) is an SNMP trap handler written in Perl for use with the Net-SNMP. Easy to setup and use. |
| snort | Snort is an open source network intrusion prevention and detection system (IDS/IPS). Combining the benefits of signature, protocol, and anomaly-based inspection. |
| softflowd | Softflowd is flow-based network traffic analyser capable of Cisco NetFlow data export. Softflowd semi-statefully tracks traffic flows recorded by listening on a network interface or by reading a packet capture file. These flows may be reported via NetFlow to a collecting host or summarised within softflowd itself. Softflowd supports Netflow versions 1, 5, 9 and 10 (IPFIX) and is fully IPv6-capable - it can track IPv6 flows and send export datagrams via IPv6. It also supports export to multicast groups, allowing for redundant flow collectors. |
| squid | High performance web proxy cache (3.5 branch). It combines Squid as a proxy server with its capabilities of acting as a HTTP / HTTPS reverse proxy. It includes an Exchange-Web-Access (OWA) Assistant, SSL filtering and antivirus integration via C-ICAP. |
| squidGuard | High performance web proxy URL filter. |
| Status_Traffic_Totals | Traffic Totals page under the Status menu, which will give a total amount of traffic passed In/Out over the period of hours, days, and months. Uses vnStat for data collection. |
| stunnel | SSL encryption wrapper between remote client and local or remote servers. |
| sudo | sudo allows delegation of privileges to users in the shell so commands can be run as other users, such as root. |
| suricata | High Performance Network IDS, IPS and Security Monitoring engine by OISF. |
| syslog-ng | Syslog-ng syslog server. This service is not intended to replace the default pfSense syslog server but rather acts as an independent syslog server. |
| System_Patches | A package to apply and maintain custom and recommended system patches. |
| Telegraf | Telegraf is an agent written in Go for collecting, processing, aggregating, and writing metrics. |
| tftpd | tftpd installs and runs a TFTP server. We use the versatile tftp-hpa server. |
| tinc | tinc is a Virtual Private Network (VPN) daemon that uses tunnelling and encryption to create a secure private network between hosts on the Internet. Because the tunnel appears to the IP level network code as a normal network device, there is no need to adapt any existing software. This tunnelling allows VPN sites to share information with each other over the Internet without exposing any information to others. A single tinc daemon can accept more than one connection at a time, thus making it possible to create larger virtual networks, because some limitations are circumvented. Instead of most other VPN implementations, tinc encapsulates each network packet in its own UDP packet, instead of encapsulating all into one TCP or even PPP over TCP stream. This results in lower latencies, less overhead, and in general better responsiveness and throughput. LICENSE: GPL3 or later with execption to link with OpenSSL |
| udpbroadcastrelay | A GUI for UDP Broadcast Relay. This program listens for UDP broadcast packets and retransmits on additional interfaces. |
| zabbix-agent4 | Zabbix agent is deployed on a monitoring target to actively monitor local resources and applications (hard drives, memory, processor statistics etc). The agent gathers operational information locally and reports data to Zabbix server for further processing. In case of failures (such as a hard disk running full or a crashed service process), Zabbix server can actively alert the administrators of the particular machine that reported the failure. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zabbix-agent5 | Zabbix agent is deployed on a monitoring target to actively monitor local resources and applications (hard drives, memory, processor statistics etc). The agent gathers operational information locally and reports data to Zabbix server for further processing. In case of failures (such as a hard disk running full or a crashed service process), Zabbix server can actively alert the administrators of the particular machine that reported the failure. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zabbix-agent6 | Zabbix agent is deployed on a monitoring target to actively monitor local resources and applications (hard drives, memory, processor statistics etc). The agent gathers operational information locally and reports data to Zabbix server for further processing. In case of failures (such as a hard disk running full or a crashed service process), Zabbix server can actively alert the administrators of the particular machine that reported the failure. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zabbix-agent64 | Zabbix agent is deployed on a monitoring target to actively monitor local resources and applications (hard drives, memory, processor statistics etc). The agent gathers operational information locally and reports data to Zabbix server for further processing. In case of failures (such as a hard disk running full or a crashed service process), Zabbix server can actively alert the administrators of the particular machine that reported the failure. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zabbix-proxy4 | A Zabbix proxy can collect performance and availability data on behalf of the Zabbix server. This way, a proxy can take on itself some of the load of collecting data and offload the Zabbix server. Also, using a proxy is the easiest way of implementing centralized and distributed monitoring, when all agents and proxies report to one Zabbix server and all data is collected centrally. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zabbix-proxy5 | A Zabbix proxy can collect performance and availability data on behalf of the Zabbix server. This way, a proxy can take on itself some of the load of collecting data and offload the Zabbix server. Also, using a proxy is the easiest way of implementing centralized and distributed monitoring, when all agents and proxies report to one Zabbix server and all data is collected centrally. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zabbix-proxy6 | A Zabbix proxy can collect performance and availability data on behalf of the Zabbix server. This way, a proxy can take on itself some of the load of collecting data and offload the Zabbix server. Also, using a proxy is the easiest way of implementing centralized and distributed monitoring, when all agents and proxies report to one Zabbix server and all data is collected centrally. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zabbix-proxy64 | A Zabbix proxy can collect performance and availability data on behalf of the Zabbix server. This way, a proxy can take on itself some of the load of collecting data and offload the Zabbix server. Also, using a proxy is the easiest way of implementing centralized and distributed monitoring, when all agents and proxies report to one Zabbix server and all data is collected centrally. Zabbix is an enterprise-class open source distributed monitoring solution. |
| zeek | Zeek (formerly Bro) is a passive, open-source network traffic analyzer. It detects specific attacks, including those defined by signatures or events, as well as unusual activity. |
OPNsense Plugins
| Package Name | Description |
|---|---|
| os-acme-client | ACME Client |
| os-apcupsd | APCUPSD - APC UPS daemon |
| os-bind | BIND domain name service |
| os-c-icap | c-icap connects the web proxy with a virus scanner |
| os-cache | Webserver cache |
| os-caddy | Easy to configure Reverse Proxy with Automatic HTTPS and Dynamic DNS |
| os-chrony | Chrony time synchronisation |
| os-clamav | Antivirus engine for detecting malicious threats |
| os-collectd | Collect system and application performance metrics periodically |
| os-crowdsec | Lightweight and collaborative security engine |
| os-ddclient | Dynamic DNS client |
| os-debug | Debugging Tools |
| os-dec-hw | Deciso hardware specific information |
| os-dmidecode | Display hardware information on the dashboard |
| os-dnscrypt-proxy | Flexible DNS proxy supporting DNSCrypt and DoH |
| os-etpro-telemetry | ET Pro Telemetry Edition |
| os-freeradius | RADIUS Authentication, Authorization and Accounting Server |
| os-frr | The FRRouting Protocol Suite |
| os-ftp-proxy | Control ftp-proxy processes |
| os-git-backup | Track config changes using git |
| os-google-cloud-sdk | Google Cloud SDK |
| os-grid_example | A sample framework application |
| os-haproxy | Reliable, high performance TCP/HTTP load balancer |
| os-helloworld | A sample framework application |
| os-hw-probe | Collect hardware diagnostics |
| os-igmp-proxy | IGMP-Proxy Service |
| os-intrusion-detection-content-et-open | IDS Proofpoint full ET open ruleset complementary subset for ET Pro Telemetry edition |
| os-intrusion-detection-content-et-pro | IDS Proofpoint ET Pro ruleset (needs a valid subscription) |
| os-intrusion-detection-content-snort-vrt | IDS Snort VRT ruleset (needs registration or subscription) |
| os-iperf | Connection speed tester |
| os-lcdproc-sdeclcd | LCDProc for SDEC LCD devices |
| os-lldpd | LLDP allows you to know exactly on which port is a server |
| os-maltrail | Malicious traffic detection system |
| os-mdns-repeater | Proxy multicast DNS between networks |
| os-munin-node | Munin monitoring agent |
| os-net-snmp | Net-SNMP is a daemon for the SNMP protocol |
| os-netdata | Real-time performance monitoring |
| os-nextcloud-backup | Track config changes using NextCloud |
| os-nginx | Nginx HTTP server and reverse proxy |
| os-node_exporter | Prometheus exporter for machine metrics |
| os-nrpe | Execute nagios plugins |
| os-ntopng | Traffic Analysis and Flow Collection |
| os-nut | Network UPS Tools |
| os-openconnect | OpenConnect Client |
| os-OPNProxy | OPNsense proxy additions |
| os-postfix | SMTP mail relay |
| os-puppet-agent | Manage Puppet Agent |
| os-qemu-guest-agent | QEMU Guest Agent for OPNsense |
| os-radsecproxy | RADIUS proxy provides both RADIUS UDP and TCP/TLS (RadSec) transport |
| os-realtek-re | Realtek re(4) vendor driver |
| os-redis | Redis DB |
| os-relayd | Relayd Load Balancer |
| os-rfc2136 | RFC-2136 Support |
| os-rspamd | Protect your network from spam |
| os-shadowsocks | Secure socks5 proxy |
| os-siproxd | Siproxd is a proxy daemon for the SIP protocol |
| os-smart | SMART tools |
| os-squid | Squid is a caching proxy for the web |
| os-sslh | sslh configuration front-end |
| os-stunnel | Stunnel TLS proxy |
| os-sunnyvalley | Vendor Repository for Zenarmor (a.k.a Sensei, Next Generation Firewall Extensions) |
| os-tayga | Tayga NAT64 |
| os-telegraf | Agent for collecting metrics and data |
| os-tftp | TFTP server |
| os-theme-cicada | The cicada theme - dark grey onyx |
| os-theme-rebellion | A suitably dark theme |
| os-theme-tukan | The tukan theme - blue/white |
| os-theme-vicuna | The vicuna theme - blue sapphire |
| os-tinc | Tinc VPN |
| os-tor | The Onion Router |
| os-udpbroadcastrelay | Control udpbroadcastrelay processes |
| os-upnp | Universal Plug and Play (UPnP IGD & PCP/NAT-PMP) Service |
| os-virtualbox | VirtualBox guest additions |
| os-vmware | VMware tools |
| os-vnstat | Network traffic monitor |
| os-wazuh-agent | Agent for the open source security platform Wazuh |
| os-web-proxy-sso | Kerberos authentication module |
| os-wol | Wake on LAN Service |
| os-xen | Xen guest utilities |
| os-zabbix-agent | Zabbix monitoring agent |
| os-zabbix5-proxy | Zabbix monitoring proxy |
| os-zabbix6-agent | Zabbix monitoring agent |
| os-zabbix6-proxy | Zabbix monitoring proxy |
| os-zabbix64-agent | Zabbix monitoring agent |
| os-zabbix64-proxy | Zabbix monitoring proxy |
| os-zerotier | Virtual Networks That Just Work |
Licensing and Cost
Licensing Models
- pfSense CE: Released under the Apache License 2.0. Netgate also offers a commercial version with additional features (pfSense Plus).
- OPNsense: Released under the BSD license, promoting open-source freedom and flexibility.
Cost Considerations
- pfSense CE: Free to use with optional commercial support.
- OPNsense: Entirely open-source and free, with optional commercial support available from Deciso.
Licensing and Commercial Use
Licensing is a critical aspect to consider when choosing between pfSense CE and OPNsense, as it impacts how you can use, modify, and distribute the software.
pfSense CE Licensing
- License Type: Apache License 2.0
- The Apache License 2.0 is a permissive free software license that allows users to use, modify, and distribute the software under the terms of the license. This includes commercial use.
- Key Permissions:
- Commercial Use: The software can be used for commercial purposes.
- Modification: Users can modify the software and distribute the modified version.
- Distribution: The software can be freely distributed.
- Patent Use: Grants rights to use any patents the contributors may hold that are essential to the software.
- Requirements:
- Attribution: The original authors must be credited.
- Notice: The license notice and copyright statement must be included in all copies or substantial portions of the software.
- State Changes: If the software is modified, the changes must be documented.
- Trademark Restrictions:
- The Apache 2.0 license only applies to the software, not the pfSense name and logo, which are trademarks.
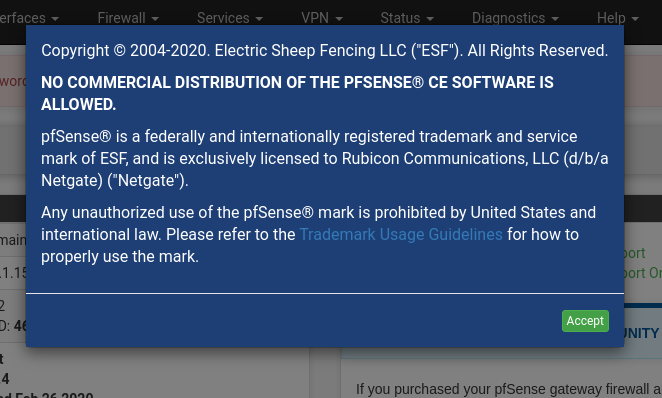
- Commercial Redistribution Restrictions: You cannot offer commercial redistribution of pfSense software without prior written permission from ESF (Electric Sheep Fencing, LLC), which involves not offering services like “Installation of pfSense software” or selling devices pre-loaded with pfSense software without permission.
- Examples:
- A consultant may offer firewall services without mentioning pfSense or using its logo in advertising.
- A customised distribution of pfSense software can be made with a different name and logo, as long as the relationship to pfSense is clearly stated.
- Build Tools: The build tools for pfSense are not fully open-source, which means replicating or modifying the build process may be a struggle.
The following notice appear in the web interface:
OPNsense Licensing
- License Type: BSD License
- The BSD license is a permissive free software license that imposes minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. It allows individuals and companies to use, modify, and distribute the software with minimal restrictions.
- Key Permissions:
- Commercial Use: The software can be used for commercial purposes.
- Modification: Users can modify the software and distribute the modified version.
- Distribution: The software can be freely distributed.
- Requirements:
- Attribution: The original authors must be credited.
- No Warranty: The license typically disclaims warranties, limiting liability for the authors.
Security and Privacy
Regulatory Compliance
- pfSense CE: Compliance with various regulatory requirements is possible, but users must ensure configurations meet specific standards.
- OPNsense: Emphasises GDPR compliance and privacy, aligning with EU regulations.
Security Practices
- pfSense CE: Regular updates and security patches, though the focus may increasingly shift to pfSense Plus.
- OPNsense: Frequent updates and a strong focus on security, with a transparent process for handling vulnerabilities.
Updates and Features
OPNsense
It’s crucial to consider how updates and changes are managed and distributed. For OPNsense, most of the significant updates and changes occur first in the base version. These enhancements are then ported to the Business Edition, ensuring that the community-driven version remains robust and up-to-date. This approach fosters a strong open-source ethos, where the community benefits directly from the latest developments.
pfSense CE
In contrast, pfSense follows a different model. The majority of updates and new features are initially introduced in pfSense Plus, the commercial version of the software. Some of these improvements are subsequently ported back to pfSense CE, the community edition. However, not all changes make their way into the CE version, which can result in a feature disparity between the two versions. This approach reflects Netgate’s strategy of prioritising its commercial offering while still maintaining a viable community edition.
Case Studies and User Feedback
Real-world Applications
- pfSense CE: Widely used in both small business and enterprise environments, known for its robustness and reliability.
- OPNsense: Also popular in diverse settings, praised for its ease of use and strong feature set.
User Reviews and Feedback
- pfSense CE: Users appreciate its comprehensive feature set and reliability but note a steeper learning curve and concerns about the future focus on pfSense Plus.
- OPNsense: Often lauded for its user-friendly interface and active development community, making it accessible for new users.
Popularity and Trends
In addition to comparing the features, usability, and support options of pfSense CE and OPNsense, it’s also important to consider their popularity and adoption trends over time. Understanding which firewall solution is more commonly searched for and potentially more widely used can provide insights into community support, available resources, and overall market preference.
Let’s analyse the popularity of pfSense CE and OPNsense using Google Trends data from the past five years, offering a statistical overview of how each has been perceived and adopted by users globally.
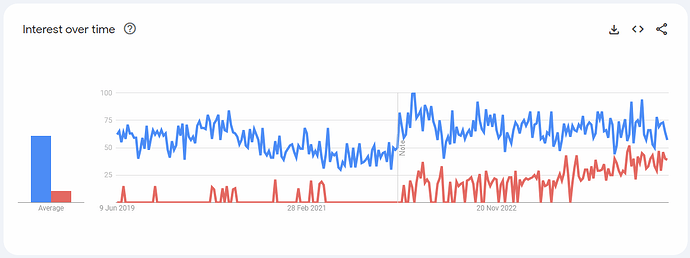
Last 5 Years: UK
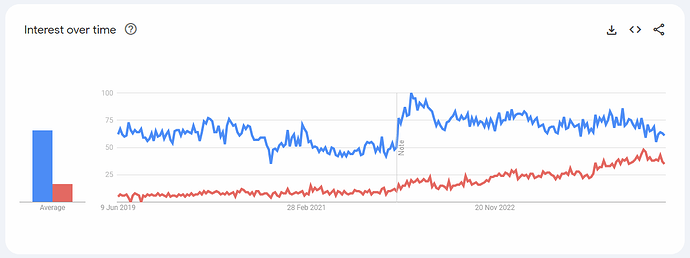
Last 5 Years US
Source: Google Trends.
The highest bump for OPNsense is around October 2023 when the Plus-no-longer-free thing started, which also shows a decline for pfSense; suggesting that people want to look for open free software.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Differences
- pfSense CE is backed by a US company (Netgate) and has a more centralized development approach, whereas OPNsense is EU-based (Deciso) and emphasizes community-driven development.
- The recent introduction of pfSense Plus may divert attention and resources from pfSense CE.
- OPNsense was recommended as the go-to solution following the end of the m0n0wall project.
- OPNsense generally offers a more modern and user-friendly interface compared to pfSense CE.
- Both provide strong security features, but OPNsense includes built-in two-factor authentication.
- OPNsense offers a robust API for automation and integration, while pfSense CE lacks an official API.
- The build tools for pfSense are not fully open-source, which may limit customization options.
Choosing the Right (Open Source) Solution
- If considering commercial support options, choosing a company in the appropriate location and timezone can
- Do you need the business offering or not?
Community Involvement and Open Source Philosophy:
- OPNsense might be more suitable for those